Deburring
Deburring refers to the removal of burrs and flashes, as well as the blunting and rounding of sharp edges.
A burr or flash is defined as a sharp protrusion on the surface of a material, created during the process of forming various objects..
The deburring process is most often used on machine parts and semi-finished products made by machining (after turning, milling, drilling) as well as castings, mouldings or forgings.
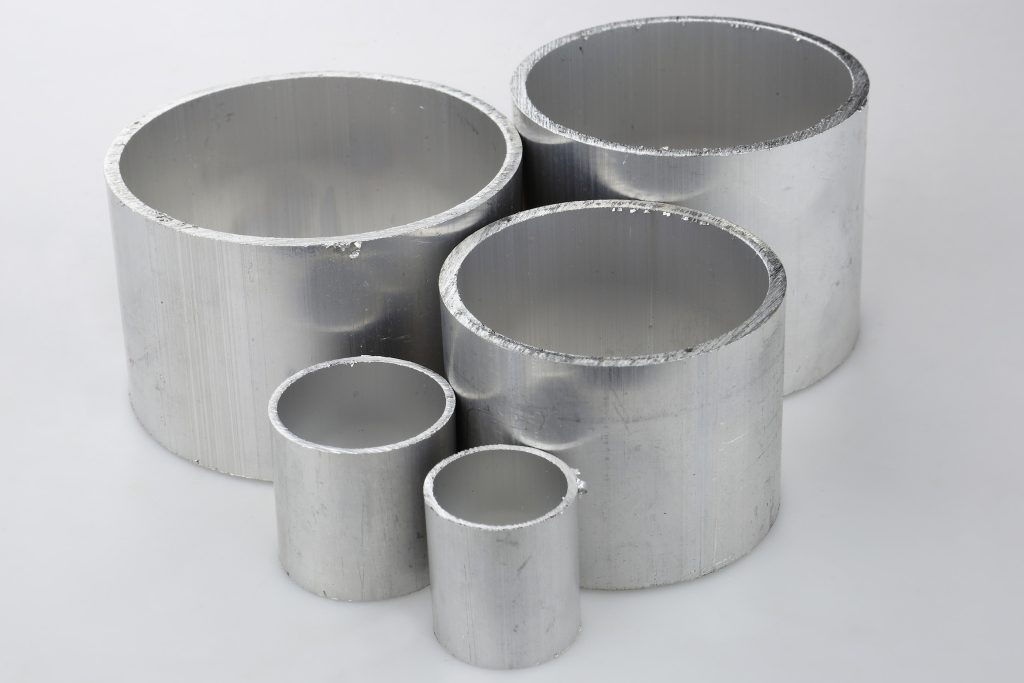
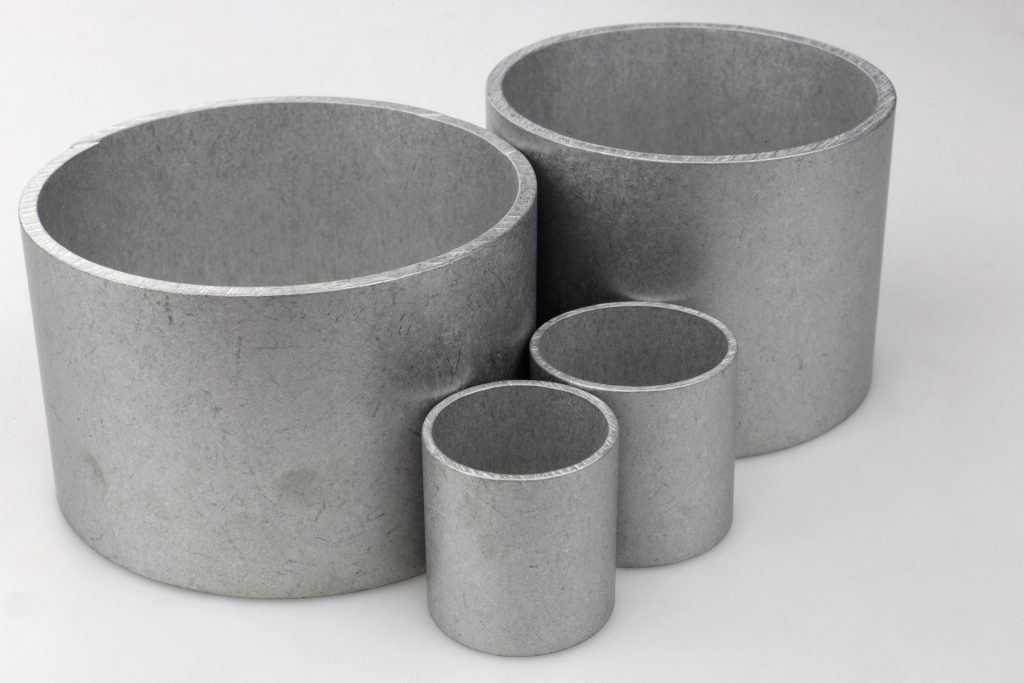


Burrs and flash must be removed for several important reasons:
- obtaining a specific dimensional accuracy of the object,
- product aesthetics,
- safety of use (prevention of injuries from sharp edges of the object).
Flashes are created during centrifugal/pressure casting of non-ferrous metals, plastic objects and during the production of various types of rubber products.
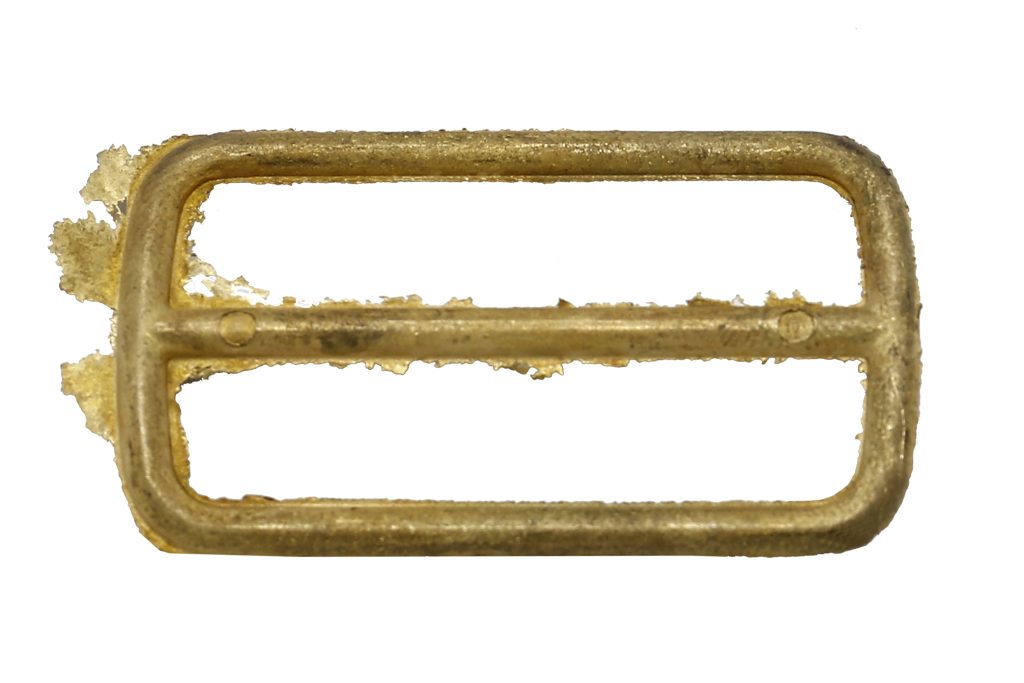
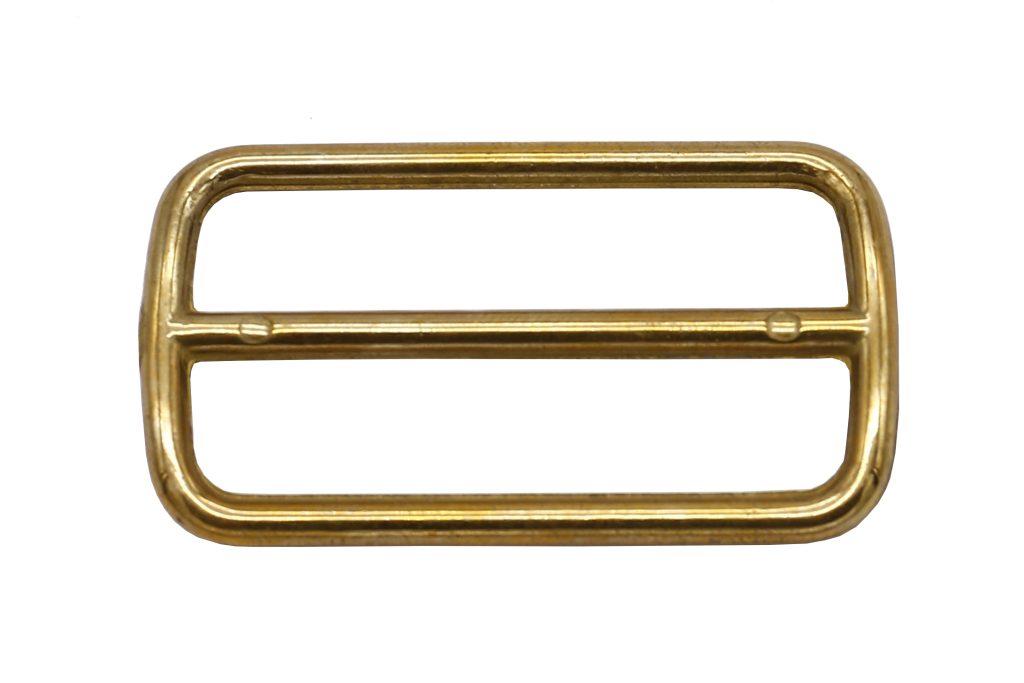
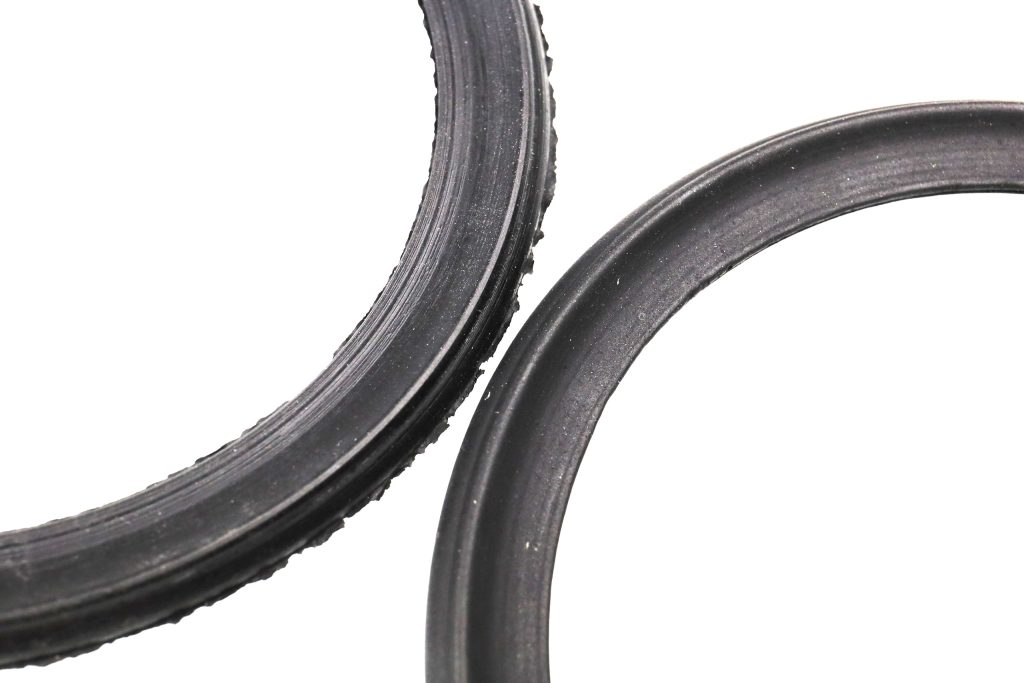



There are many methods of removing burrs, including: manual processing using various tools such as a deburrer, a countersink or a scraper, or abrasive blasting, abrasive press or vibro-abrasive processing, commonly known as tumbling.
Vibroabrasive processing is used for mass-produced items because it significantly shortens the production time and therefore costs compared to manual machining. Machines used for the deburring process are round vibratory machines, trough vibratory machines and disc finishing machines.
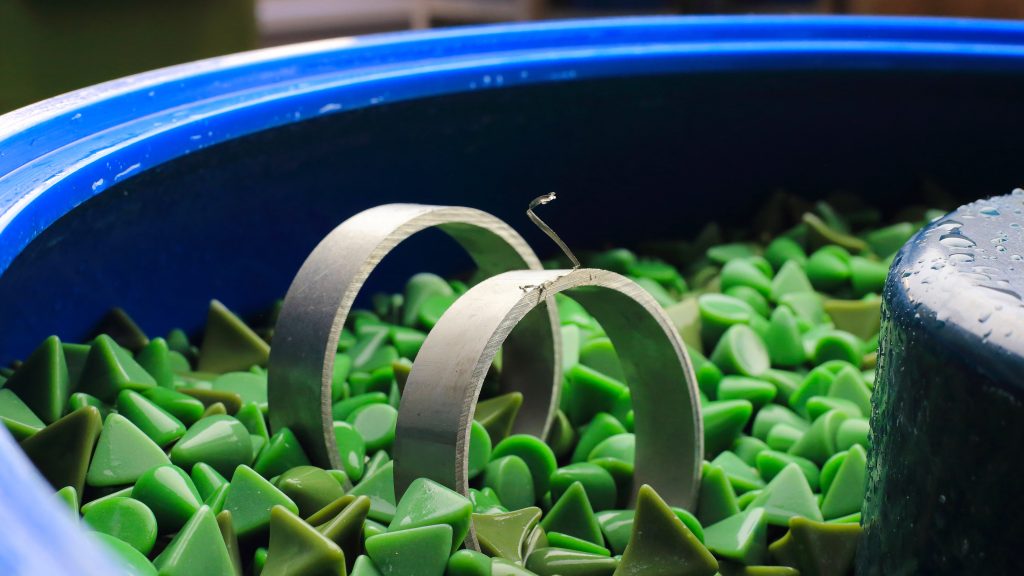

The advantages of deburring in vibro-abrasive machines include:
- speed of the process,
- repeatability of results,
- minimal operator involvement.
Deburring in vibro-abrasive machines is carried out using abrasive media with cutting properties adapted to the type of material being processed. Ceramic chips with high or medium cutting properties are used to remove burrs and round off sharp edges of metal objects. Plastic chips are used to process brass, bronze, aluminum and zinc alloys.